A Milestone by UW–Madison Researchers: 3D-printed brain tissue
A team at the University of Wisconsin–Madison has unveiled a ground-breaking accomplishment that represents a quantum leap forward in neuroscience and health technology: the world’s first 3D-printed brain tissue that functions similarly to natural brain matter. This ground-breaking discovery opens the door to ground-breaking discoveries in the knowledge and treatment of neurological and neurodevelopmental disorders.
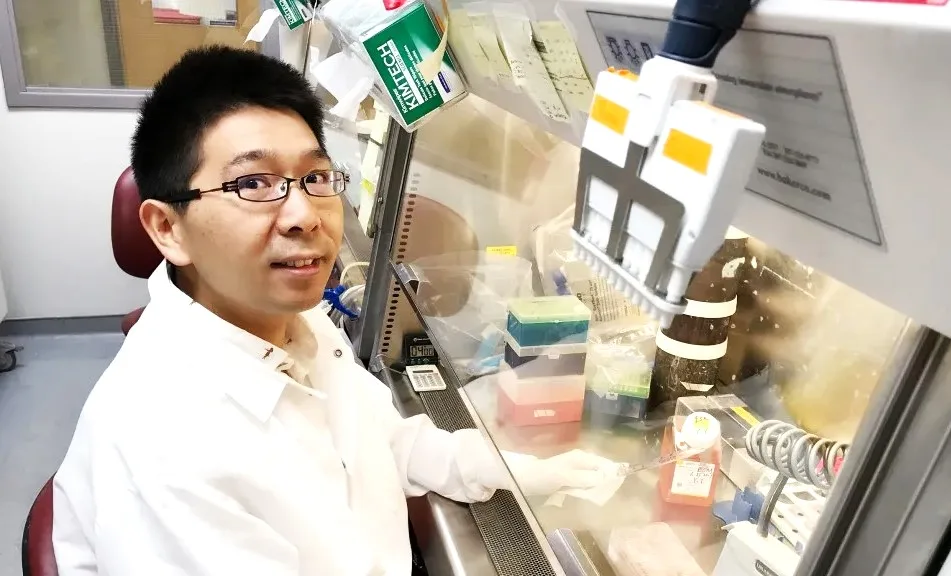

A Leap Towards Understanding the Brain
For years, the intricacies of the human brain have puzzled scientists. Its complex networks and the delicate balance of its functioning stand as a formidable challenge in the study of neurological conditions, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. The team at UW–Madison, however, has taken a significant step towards demystifying this complexity by developing 3D-printed brain tissue that not only grows but also functions akin to typical brain tissue.
This achievement holds vast implications for researchers dedicated to exploring the brain’s mysteries and developing treatments for a wide spectrum of neurological conditions. The ability to replicate brain tissue’s functional aspects opens new doors to understanding how brain diseases develop and progress.
Innovation in 3D Printing
Central to this development is an innovative 3D printing technique that employs a soft ‘bio-ink’ gel, coupled with a strategic horizontal positioning of brain cells. This method fosters an environment where cells can communicate, signal, and network as they would within a natural brain setting. The precision and adaptability of this printed brain tissue offer unparalleled opportunities for delving into brain studies and tackling its disorders.
The implications extend beyond understanding diseases; they revolutionize drug testing. With functional human brain tissue at their disposal, scientists can gain insight into how potential drugs impact the human brain, significantly enhancing the precision and effectiveness of drug testing protocols.
Beyond Organoids: A New Horizon
Distinguishing itself from brain organoids, the UW–Madison team’s approach allows for meticulous control over cell types and their spatial arrangement. This not only enables neurons to intertwine and commence communication but also provides a more accurate model for investigating various neurological issues and brain functions. Such an approach promises to yield deeper insights into the workings of the brain and its diseases, marking a considerable stride towards understanding and treating neurological disorders.
Setting a Benchmark in Neuroscience
The creation of functional 3D-printed brain tissue by the UW–Madison scientists represents a significant milestone in the future of health technology. Backed by numerous research organizations and foundations, this breakthrough showcases the immense potential of 3D printing technology in healthcare. It highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research and technological innovation in unraveling the complexities of the human brain and forging new paths in the development of treatments for neurological disorders.
In conclusion, the development of 3D-printed functional brain tissue by UW–Madison researchers not only sets a new benchmark in the field of neuroscience but also exemplifies how cutting-edge technology can revolutionize our approach to health care and disease treatment. This breakthrough offers hope for the future, promising advancements in the understanding and treatment of brain-related disorders, and underscores the limitless possibilities of technological innovation in improving human health.
You cover more helpful info than I have read elsewhere. Do you want to share your sourceexperience with us?
I read through this and found it useful.
Thank you so much for sharing this insightful post! Your depth of understanding on the topic is truly commendable. It’s rare to come across a piece that is both informative and engaging. Your eloquent writing style made it a pleasure to read. I eagerly look forward to your future posts.
The breadth of The knowledge is amazing. Thanks for sharing The insights with us.
Stumbling upon The article was a highlight of my day. It was just what I needed to read.
This post is a testament not only to The expertise but also to The dedication. Truly inspiring.
Compelling read with well-presented arguments. I almost felt persuaded. Almost.
The ability to convey nuanced ideas with clarity is as alluring as a whispered secret.
The thoughtful analysis has really made me think. Thanks for the great read!
I feel that is among the most important info for me. And i am satisfied studying your article. But wanna statement on few normal things, The web site style is wonderful, the articles is really great : D. Excellent task, cheers
Thank you for another informative site. Where else could I get that type of info written in such an ideal way? I have a project that I’m just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to learn more of your helpful information. Thank you for the post. I will certainly comeback.
Hiya, I’m really glad I’ve found this information. Today bloggers publish only about gossips and net and this is really annoying. A good website with exciting content, this is what I need. Thank you for keeping this website, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can’t find it.
hello!,I like your writing very so much! share we keep in touch extra about your article on AOL? I require an expert in this area to resolve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Taking a look ahead to peer you.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.