The Patagonian Mara
Known by its scientific name, Dolichotis patagonum, the Patagonian mara is an intriguing rodent found in the dry steppes of Argentina. These nocturnal mammals resemble a cute cross between a guinea pig and a rabbit. They are distinguished from other rodents by their distinctive physical characteristics and interesting way of life. We will examine the habitat, way of life, and conservation initiatives required to preserve this unique species as we delve into the world of the Patagonian mara.
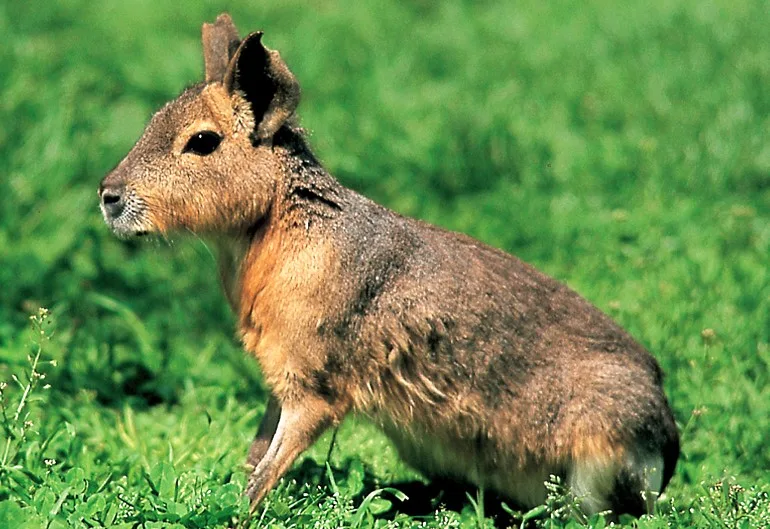

Physical attributes and features:
The maras of Paraguay are not your typical rodents. Their bodies are similar to hoofed animals, and they have hare-like legs and ears. But there’s no denying that their faces resemble those of their close relatives, the capybaras. They have thick, fine-textured coats that are mostly grayish-brown in color, with a noticeable white patch on the stomach and orange splotches on their cheeks and chests. Maras weigh between 16 and 20 pounds, with males being slightly larger than females. Their long limbs allow them to reach remarkable speeds of up to 35 miles per hour. Their large ears aid in predator detection and temperature regulation.
Lifestyle and Reproduction:
The lifestyle of Patagonian maras is truly unique due to their monogamous nature. Bonded pairs, which are made for life, travel and live together, with the female determining when to graze, rest, or move. These couples remain intimate, but they don’t often come into contact physically outside of mating situations. They raise their young in group burrows that can hold up to 30 pups as a means of protection. Once a day for approximately an hour, females, who can identify their offspring by scent and vocalizations, carefully examine pups before letting them nurse. Before emerging to forage alongside their parents, pups spend the first six weeks of their lives in the burrow.
Range and Habitat:
Patagonian maras live across Argentina in various biomes: the Monte Desert, Las Pampas, and the region named Patagonia. They’ve adapted to semi-arid open areas, thriving in temperate lowland habitats like grasslands and shrublands.
Diet:
In the wild, Patagonian maras eat grasses and shrub leaves and occasionally forage for fruit. In captivity, they are fed vegetables, browse (edible plant material), and commercially made rodent chow.
Conservation:
Habitat destruction for hunting and agriculture has caused localized extinctions and population declines. To help with conservation, people can buy locally grown produce to prevent habitat loss from crop conversion. Participating in programs like Meatless Mondays can also aid in preserving mara habitat, especially in Argentina, known for its beef cattle sector.
The Patagonian mara is a unique species with captivating physical features. It leads a monogamous lifestyle and prefers habitats in Argentina’s arid steppes. To ensure the survival of this intriguing species, we can contribute to their conservation by learning about and appreciating these extraordinary rodents.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
beatae sed qui molestias ut sapiente excepturi eum cum repellendus quaerat sed reprehenderit sequi voluptatibus. aut culpa et saepe odio in voluptatum quasi ratione vitae qui deserunt facilis quod id.
Gratias tibi ago pro communicandis cogitationibus tuis nobiscum. Verba tua, cum philosophicis inquisitionibus in naturam beatitudinis ac ethicae voluptatis et doloris referuntur, penitus resonant cum perpetua inquisitione complexionum humanarum experientiae.
Sententiam quam significasti – illustrando aequilibrium inter provocationes et studium voluptatis – adsimilat cum studio ad altiorem cognitionem promovendi factorum myriadum quae sensus nostros vitae valoris inducunt. Hoc admonet momentum discretionis in quaerendis ad perficiendum, ac sapien- tiam agnoscendo verum incrementum saepe evenire ex adversitate fortiter ac mollitia.
Prospectus tuus sermonem nostrum auget, et gratissimi sumus facultatem de his quaestionibus intempestiva cogitandi simul. Hunc dialogum pergamus, invicem adhortantes ad quaerendas semitas significativas, licet interdum difficiles, quae ad uberiorem exsistentiae nostrae intelligentiam ducunt.
tepidum respicit;
Find Soft News Research Team